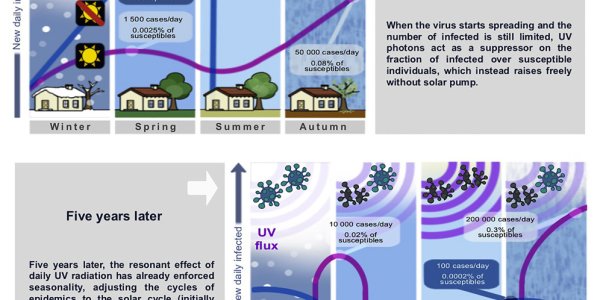
Paper Posits That Daily Solar Radiation Is A Key Factor In Epidemics
Viral respiratory epidemics like the flu spike cyclically during autumn and winter - but only in the temperate regions of the globe's northern and southern hemispheres.
In the equatorial belt, they…