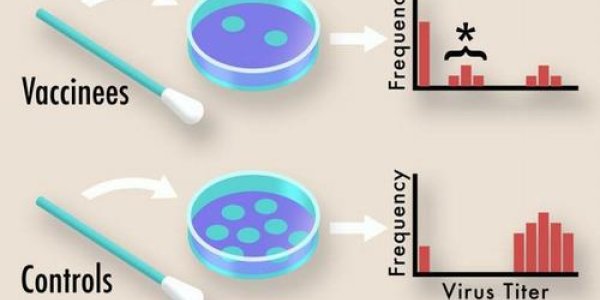
The Human Role In Spread Of 90 Percent Of Hospital Infections
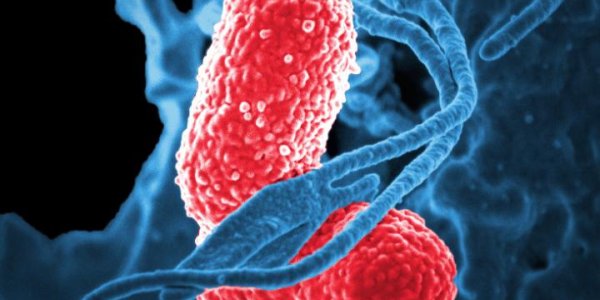
People treated in hospitals and other health care settings are increasingly at risk of infection with multidrug-resistant bacteria. Many of these microbes produce enzymes called extended-spectrum β-…