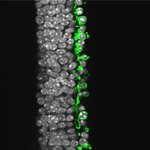
Retinitis pigmentosa are a diverse group of hereditary diseases that lead to incurable blindness and affect two million people worldwide. Though the causes are diverse, the manifestation of the disease is similar: highly sensitive rod photoreceptors, which allow us to see at dusk, die first and the cones that operate during daylight and are responsible for high-resolution color vision follow.
Scientists from the Friedrich Miescher Institute for Biomedical Research (FMI)say they have restored vision in retinitis pigmentosa using an archaebacterial protein, halorhodopsin. …


