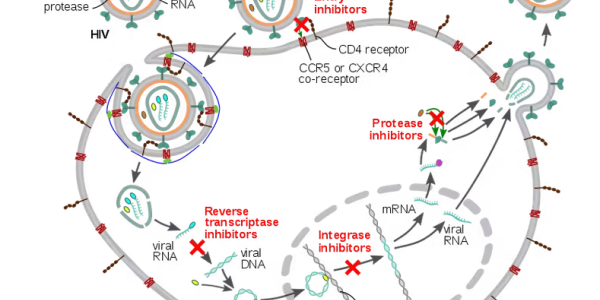
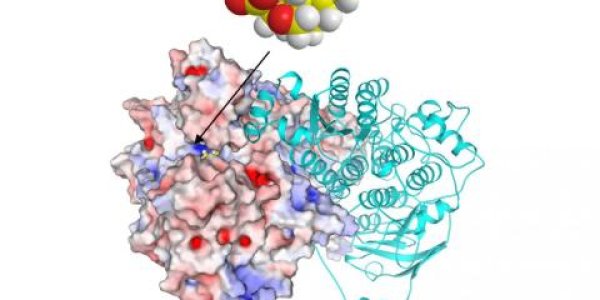
Thanks To Ancient Evolution, Your Body Makes Its Own Anti-Viral Drugs
Antiviral drugs are generally considered to be a 20th century invention. But recent research has uncovered an unexpected facet to your immune system: It can synthesize its own antiviral molecules in…