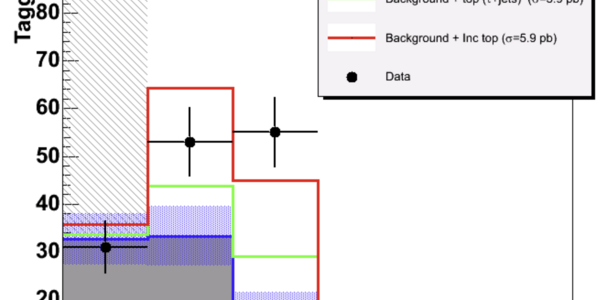
Why Measure The Top Quark Production Cross Section?
As part of my self-celebrations for XX years of blogging activities, I am reposting here (very) old articles I wrote over the years on topics ranging from Physics to Chess to anything in between. The...