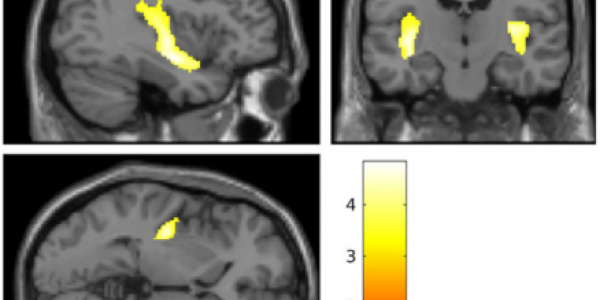
Honeybees Do Arithmetic
Bees have tiny brains but that is all relative; It seems they also possess complex number skills.
Lots of animals count as shown by how many engage in foraging, shoaling, and resource management…