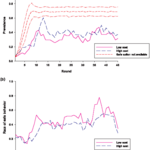
Here is a conundrum in the culture wars; genetically modified tobacco has been shown to have numerous beneficial effects and now another one has been added.
The treatment for rabies (painful shots, thankfully not all in the stomach in 2013) is not as bad as the disease (death) but it is hardly civilized, so here is hoping the anti-science crowd does not claim genetically modified tobacco will create giant rats with SuperRabies. Rabies deaths are not a big issue in the USA, 10 a year or so, and therefore it may be safe to do fundraising campaigns about Frankentobacco here, but for…