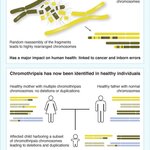
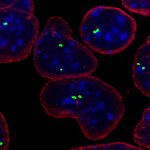
Scientists have grown the first 3-D mini lungs from stem cells, which means research is one step closer to being able to create one of the Big 5 organs from a patient's stem cells rather than having waiting lists for donors.
The University of Michigan scientists succeeded in growing structures resembling both the large proximal airways and the small distal airways.
Their recipe:
Embryonic stem cells
Proteins involved in lung development
Growth factors
Inhibitors of intestine development
Growing media
Petri dish
Protein mixture
Method for "morphogenesis in a dish"
First, add…