Astronomy & Astrophysics is publishing the first high-resolution image of the young binary system Theta1 Orionis C, located in the Orion Trapezium cluster. This image was obtained by a team of astronomers led by Stefan Kraus and Gerd Weigelt (MPIfR, Bonn, Germany), using the AMBER instrument installed at the ESO/Very Large Telescope Interferometer (VLTI). AMBER is an interferometer beam combiner for the VLT, sensitive in the near-infrared wavelength range (from 1 to 2.5 microns). Details on this instrument and on earlier results are available in previous A&A press releases (Feb. 21, 2007 and Oct. 10, 2008).
The binary star Theta1 Ori C is the brightest of the four Trapezium stars in the Orion nebula (see Fig. 1). The Orion Trapezium cluster is the nearest region where massive stars are forming, located at about 1350 light-years from us. It provides a unique laboratory for studying the formation process of massive stars in detail. The intense radiation of Theta1 Ori C ionizes the whole Orion nebula. Its strong wind also shapes the famous Orion proplyds, young stars that are still surrounded by their protoplanetary dust disks.
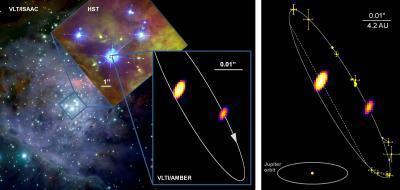
Left: Zooming into the center of the Orion star-forming region with the four bright Trapezium stars (Theta1 Orionis A-D). The dominant star is Theta1 Orionis C, which was imaged with unprecedented resolution with the VLT interferometer (lower right). Right: The orbit of the binary system (grey line) was derived using position measurements obtained over the past 12 years (yellow points). The size of the orbit of Jupiter around our sun is shown for comparison.
(Photo Credit: MPIfR (Stefan Kraus), combining the VLTI image of Theta1 Ori C with images from VLT/ISAAC (ESO) and HST (NASA, Chris O'Dell).)
Theta1 Ori C is a bright, naked-eye star, but its companion is so close (20 milli-arcseconds) that it was not detected before 1999. Thus, high-angular resolution is needed for an in-depth study of the system. The image that is now published has a sharpness of 2 milli-arcseconds, which corresponds to the apparent size of an automobile on the surface of the Moon. Combining AMBER observations with position measurements of the system over the past 12 years, the team was able to compute the orbital period of the system (11 years). Using Kepler's third law, they also derived the masses of the two stars (38 and 9 solar masses). Finally, they estimated the distance to the system, hence to the center of the Orion star-forming region (1350 light-years). These various measurements are essential for improving theoretical models of massive star formation.