Spectacular jets powered by the gravitational energy of a super massive black hole in the core of the elliptical galaxy Hercules A are shown off by the combined imaging power of the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Camera 3 and the recently upgraded Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) radio telescope in New Mexico.
Hercules A is about 2 billion light-years away, is roughly 1,000 times more massive than the Milky Way and harbors a 2.5-billion-solar-mass central black hole that is 1,000 times more massive than the black hole in the Milky Way.But the yellowish elliptical galaxy in the center of the image appears ordinary as seen by Hubble in visible wavelengths of light. However, the innocuous-looking galaxy, also known as 3C 348, has long been known as the brightest radio-emitting object in the constellation Hercules, emitting nearly a billion times more power in radio wavelengths than our Sun. It is one of the brightest extragalactic radio sources in the entire sky.
The VLA radio data reveal enormous, optically invisible jets that, at one-and-a-half million light-years wide, dwarf the visible galaxy from which they emerge. The jets are very-high-energy plasma beams, subatomic particles and magnetic fields shot at nearly the speed of light from the vicinity of the black hole. The outer portions of both jets show unusual ring-like structures suggesting a history of multiple outbursts from the super massive black hole at the center of the galaxy.
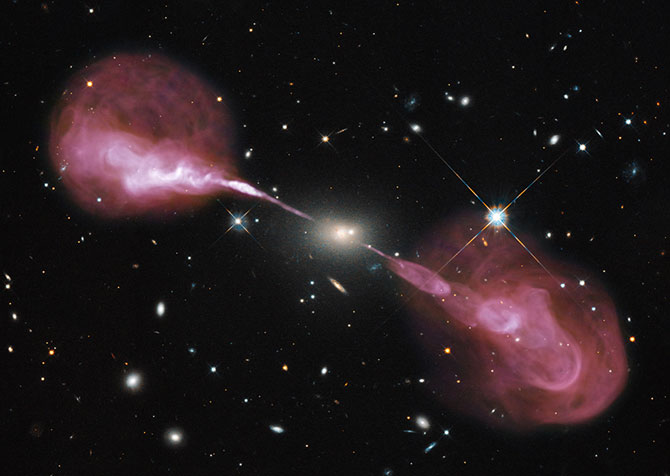
Spectacular jets powered by the gravitational energy of a supermassive black hole in the core of the elliptical galaxy Hercules A illustrate the combined imaging power of two of astronomy's cutting-edge tools, the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Camera 3, and the recently upgraded Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array radio telescope in New Mexico. Credit: NASA, ESA, S. Baum and C. O'Dea (RIT), R. Perley and W. Cotton (NRAO/AUI/NSF), and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
The innermost parts of the jets are not visible because of the extreme velocity of the material, which causes relativistic effects that beam the light away from us. Far from the galaxy, the jets become unstable and break up into the rings and wisps.
The entire radio source is surrounded by a very hot, X-ray-emitting cloud of gas, not seen in this optical-radio composite.
Hubble's view of the field also shows a companion elliptical galaxy very close to the center of the optical-radio source, which may be merging with the central galaxy. Several other elliptical and spiral galaxies that are visible in the Hubble data may be members of a cluster of galaxies. Hercules A is by far the brightest and most massive galaxy in the cluster.