The cockroach in the genus Ectobius is an invasive organism and the most common cockroach inhabiting a large region from northernmost Europe to southernmost Africa.
The fossil history of Ectobius in Europe is long, occurring in Baltic amber that is about 44 million years old, and its lineage was exclusively Old World.
But a new study says that Ectobius may have originated in the New World.
Four ancient Ectobius species were recently discovered in the 49-million-year-old Green River Formation near Rifle, Colorado in deposits that are about five million years older than the Baltic amber. However, these cockroaches soon became extinct in North America. The cause for the extinction of Ectobius in North America in the dim past is unknown, but it evidently survived in the Old World, and western Europe in particular.

44-million-year-old Ectobius balticus from northern Europe. Credit: D. S. Shcherbakov
"About 65 years ago, several entomologists in the northeastern United States noted that four species of Ectobius were present in North America," said corresponding author Dr. Conrad Labandeira. "It was always assumed that these four newcomers were the first Ectobius species to have ever lived in North America. But the discovery in Colorado proves that their relatives were here nearly 50 million years ago."
In many ways the history of Ectobius mirrors that of the biogeographic history of the horse. Horses occurred in the New World and became extinct during the late Pleistocene ecological crisis. Horses, attached to human habitation, were subsequently introduced to North America by early Spanish explorers about 11,000 years after their demise.
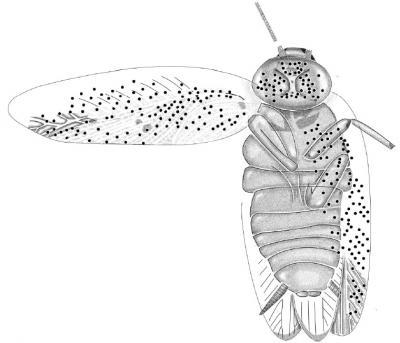
The 49-million-year-old Eocene
Ectobius kohlsi cockroach from Colorado. Credit: Peter Vršanský
This particular species is named after David Kohls, who lives near Rifle, Colorado and has been an indefatigable collector of fossil insects and plants from the nearby Green River Formation. His collection of approximately 150,000 insects from 31,000 slabs of shale now constitutes the Kohls Green River Fossil Insect Collection, which is housed in the Smithsonian's Department of Paleobiology.
Citation: Vršanský, P.; Oružinský, R.; Barna, P.; Vidlička, L'.; Labandeira, C. C., 'Native Ectobius (Blattaria: Ectobiidae) From the Early Eocene Green River Formation of Colorado and Its Reintroduction to North America 49 Million Years Later', Annals of the Entomological Society of America, Volume 107, Number 1, January 2014 , pp. 28-36(9) DOI: 10.1603/AN13042. Source: Entomological Society of America