Any road with a loose surface like or gravel or snow can develop ripples that make driving a very shaky experience. A team of physicists from Canada, France and the United Kingdom have recreated this "washboard" phenomenon in the lab with surprising results: ripples appear even when the springy suspension of the car and the rolling shape of the wheel are eliminated. The discovery may smooth the way to designing improved suspension systems that eliminate the bumpy ride.
"The hopping of the wheel over the ripples turns out to be mathematically similar to skipping a stone over water," says University of Toronto physicist, Stephen Morris, a member of the research team.
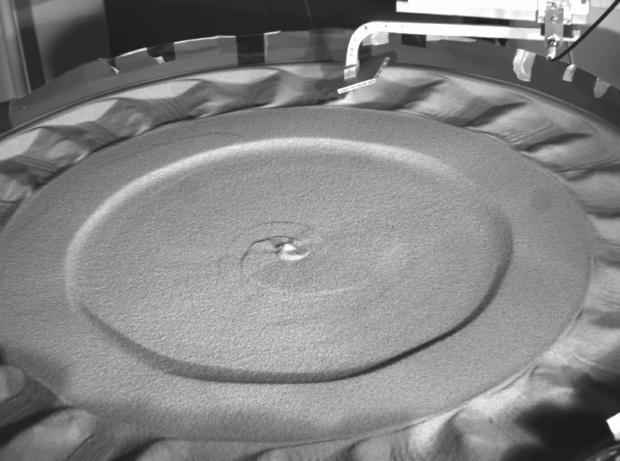

Credit: Jim McElwaine, DAMTP, Cambridge University
"To understand the washboard road effect, we tried to find the simplest instance of it, he explains. We built lab experiments in which we replaced the wheel with a suspension rolling over a road with a simple inclined plow blade, without any spring or suspension, dragging over a bed of dry sand. Ripples appear when the plow moves above a certain threshold speed."
"We analyzed this threshold speed theoretically and found a connection to the physics of stone skipping. A skipping stone needs to go above a specific speed in order to develop enough force to be thrown off the surface of the water. A washboarding plow is quite similar; the main difference is that the sandy surface "remembers" its shape on later passes of the blade, amplifying the effect."
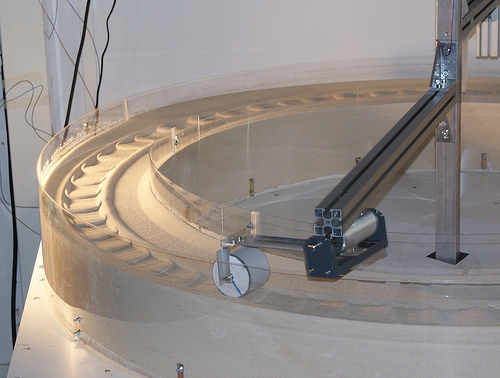
The Lyon washboard road experiment, featuring a wheel which rolls over a bed of sand, creating ripples. Experiment by Nicolas Taberlet, Ecole Normale Superieure de Lyon. Credit: Stephen Morris
Washboard road is familiar to drivers of back country roads the world over but also appears in some other surprising places in nature and technology. Just about any time a malleable surface is acted upon by a sideways force, you will get ripples. Washboard road is analogous to the little ripples that form on wind- or water-driven sand at the beach, and to the moguls which develop on ski hills. Motocross bikes and snowmobiles also make ripples. Washboard can also cause tiny bumps on steel railway tracks and even the read head in a hard disk can sometimes hop along the surface of the disk to make a washboard pattern.
In addition to Morris, the research collaboration includes lead author Anne-Florence Bitbol and Nicolas Taberlet of Ecole Normale Superieure in Lyon and Jim McElwaine of the University of Cambridge. Experiments were done in Cambridge and Lyon and results published in Physical Review E on June 26, 2009.