A century-old dream of neuroscientists to visualize a memory has been fulfilled, as University of California, Irvine researchers, using newly developing microscopic techniques, have captured first-time images of the changes in brain cell connections following a common form of learning.
The study shows that synaptic connections in a region of rats’ brains critical to learning change shape when the rodents learn to navigate a new, complex environment. In turn, when drugs are administered that block these changes, the rats don’t learn, confirming the essential role the shape change plays in the production of stable memory.
“This is the first time anyone has seen the physical substrate, the ‘face,’ of newly encoded memory. We have cleared a hurdle that once seemed insurmountable,” said Gary Lynch, professor of psychiatry and human behavior at UC Irvine and leader of one of the two research teams involved in the studies.
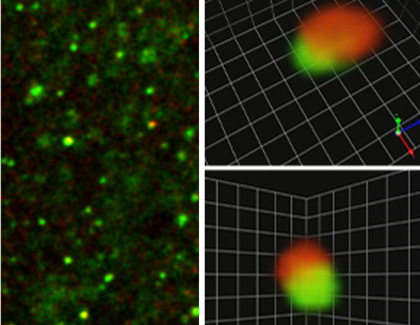
The new behavioral experiments followed a series of recent discoveries by the UC Irvine group concerning the synaptic changes responsible for long-term potentiation (LTP), a physiological effect closely related to memory storage. Those studies used brain slices from rats, maintained alive in experimental chambers, to identify chemical markers for synapses that had recently experienced the LTP effect. The new study used live animals.
Working with advanced microscopic techniques called restorative deconvolution microscopy, the UC Irvine team found that the LTP-related markers appear during learning and are associated with expanded synapses in the hippocampus. Because the size of a synapse relates to its effectiveness in transmitting messages between neurons, the new results indicate that learning improves communication between particular groups of brain cells.
The findings open the way for one of the great objectives of the life sciences: mapping the distribution of memory across brain regions. The quest for the location of memory traces, or “engrams” as they are often called, preoccupied researchers for much of the 20th century but failed because there was no way to tag synapses modified by recent learning. The new results from the UC Irvine studies remove this obstacle.
UC Irvine researchers will shortly set up a consortium of laboratories directed at producing the first maps of memory.
Vadim Fedulov, Christopher S. Rex, Danielle A. Simmons and Christine M. Gall of UC Irvine, and Linda Palmer of Carnegie Mellon University, also worked on this study, which received support from the National Institutes of Health.
Source: UC Irvine