Optics
In modern times, we have been spoiled by the ability of the private sector to make technology shrink in both cost and size - but Moore's Law can't do that forever using regular electrical signals.
Maybe it is time for Moore's Light to take over?
Engineers at have created a device that can focus light into a point just a few billionths of a meter across. Because light can carry greater amounts of data more efficiently than electrical signals traveling through copper wires, today's technology is increasingly based on optics. The world is already connected by thousands of miles of optical-…

The best way to get precise information regarding the inner structure of atoms and molecules is to excite them by means of resonant laser light but this laser light can lead to measurable modifications within the atom's electron shell, above a certain intensity. The act of getting the information changes the study.
Scientists of the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) say they have now shown experimentally how to prevent such "light shifts" and that this confirms the advantages of "hyper" Ramsey excitation that had already been predicted theoretically.
"Light shift" means that…

A device capable of amplifying the information in a single particle of light without adding noise has been created. The researchers were able to amplify the noisy quantum state of a single photon subjected to loss, without adding noise in the process - their amplification actually reduced the noise in the quantum state.
It is expected the results will stimulate further interest in the fundamental laws that govern how well amplifiers can work and in developing uses of noiseless amplification techniques for other quantum information technology applications.
Professor Geoff Pryde…

Researchers have observed the quantum regime in the interaction between nano-sized spheres of gold, thanks to the change of color of the gap between these particles when they are at distances of less than one nanometer. They have literally 'seen' a quantum kiss between nanoparticles.
The gap generated between two opposing nanospheres of gold can change its color when the distance between them is less than one 1 millionth of a millimeter (nanometer), according to recent research which confirmed that electrons accumulated on the gold surfaces around the illuminated gap between the spheres can…

New single laser devices that are the size of a virus particle can also operate at room temperature. These plasmonic nanolasers could be readily integrated into silicon-based photonic devices, all-optical circuits and nanoscale biosensors.
We're going to need ultra-fast data processing and ultra-dense information storage by the time Halo 8 comes to a holodeck near you, so reducing the size of photonic and electronic elements is critical.
"Coherent light sources at the nanometer scale are important not only for exploring phenomena in small dimensions but also for realizing optical…

If one beam travels a fixed length and another travels an extra distance or in some other slightly different way, the two light beams overlap and interfere when they meet up, creating an interference pattern that scientists inspect to obtain highly precise measurements.
Atom interferometry, however, hinges on quantum mechanics, the theory that describes how matter behaves at sub-microscopic scales. Just as waves of light can act like photons - particles - atoms can be cajoled into acting like waves if cooled to near absolute zero. At those frigid temperatures, which scientists achieve by…

A recent placebo-controlled study showed evidence of trans-cranial bright light's effect to brain functions when administered through the ear. Bright light stimulation was found to increase activity in brain areas related to processing of visual sensory information and tactile stimuli. The findings are the first ever published scientific article about functional modulation of the brain with bright light delivered to the brain through the ears.
The study was conducted with 51 healthy test subjects, utilizing functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Some of the test subjects were given…

Your cay may soon have a new dashboard, one made of a flexible plastic and oxide layer that could be integrated into the car front window to give the driver direct information
The MULTIFLEXIOXIDES project is designed to develop new cost-efficient, long lasting, light, flexible and transparent devices (can anything be all of those? Only in academia) which can display information directly on the windshield. This is possible using small glass pads with a transparent substrate of nano-sized flexible oxides, which act as a basis for organic LEDs (light-emitting diodes).
The aim of the…
A new imaging system uses walls, doors or floors as 'mirrors' to gather information about scenes that it can't see, even though those objects are not reflective.
Yes, it could ultimately lead to imaging systems that allow emergency responders to evaluate dangerous environments or vehicle navigation systems that can negotiate blind turns, among other applications, but spying on people sounds like more fun.
The system uses a femtosecond laser, which emits bursts of light so short that their duration is measured in quadrillionths of a second. To peer into a room that’s outside its line of sight…

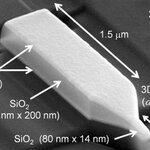
A new high-precision 3-D printer at TU Vienna is orders of magnitude faster than similar devices and opens up completely new areas of application, such as in medicine. "Two-photon lithography" means tiny structures on a nanometer scale can be fabricated quicker than ever.
Their 3-D printer uses a liquid resin, which is hardened at precisely the correct spots by a focused laser beam. The focal point of the laser beam is guided through the resin by movable mirrors and leaves behind a polymerized line of solid polymer, just a few hundred nanometers wide. This high resolution enables the creation…