Researchers have identified factors that spark the formation of pluripotent cells. Their findings, published in Developmental Cell, shed light on human embryonic development and help research into cell reprogramming and assisted conception.
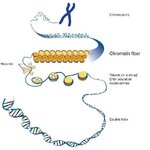
Embryonic stem cells are widely known for their ability to differentiate into any cell type - a state called pluripotency. This state is short lived in the embryo, but is essential to normal development. In this study, the researchers mapped when and where genes were expressed (turned on or off) during early development of the mouse and common marmoset, a…