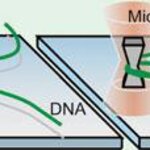
Japanese scientists have made a micro-sized sewing machine to sew long threads of DNA into shape. The work published in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal Lab on a Chip demonstrates a unique way to manipulate delicate DNA chains without breaking them.
Scientists can diagnose genetic disorders such as Down's syndrome by using gene markers, or "probes", which bind to only highly similar chains of DNA. Once bound, the probe's location can be easily detected by fluorescence, and this gives information about the gene problem.
Detecting these probes is often a slow and difficult process,…

