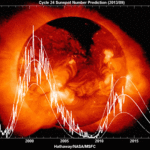
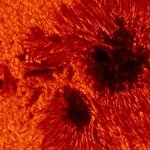
The solar system is crowded with small objects like asteroids and comets, and most have stable orbits which keep them out of harm’s way, but a small proportion of them are in orbits that risk collision with planets.
Smaller objects are more numerous and therefore result in more frequent collisions. The recent meteor seen over Chelyabinsk, Russia, in February 2013, was rare because the object was relatively large, around 17 meters across. However, the giant planet Jupiter is a much bigger target due to its tremendous gravitational attraction -- and it gets hit far more often than the Earth.…