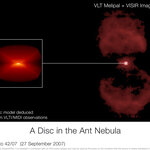
Using ESO's Very Large Telescope Interferometer and its unique ability to see small details, astronomers have uncovered a flat, nearly edge-on disc of silicates in the heart of the magnificent Ant Nebula. The disc seems, however, too 'skinny' to explain how the nebula got its intriguing ant-like shape.
The Ant Nebula is located about 5 000 light-years away. The central star is as bright as 10,000 Suns and has a temperature of 35, 000 degrees Celsius. It is the last phase before this solar-like star will become a white dwarf.
The Ant Nebula is one of the most striking planetary nebulae known…




