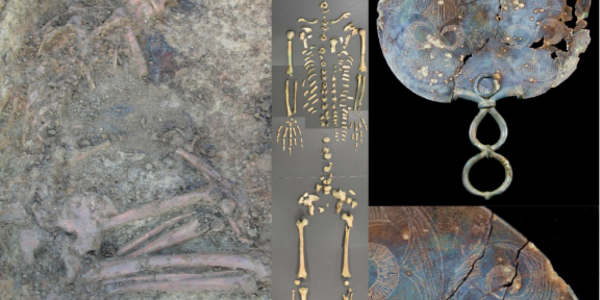
In British Iron Age Culture, Margaret Thatcher Was The Norm
In British Iron Age society, land was inherited through the female line and husbands moved to live with the wife’s community. Strong women like Margaret Thatcher resulted.That was inferred due to DNA...