A case report published in PLoS Medicine describes a rare side effect of human fetal stem cell therapy. Ninette Amariglio and Gideon Rechavi from the Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel, and colleagues report the case of a boy with a rare genetic disease, Ataxia Telangiectasia, who underwent human fetal stem cell therapy at an unrelated clinic in Moscow and who, four years after the therapy began, was shown to have abnormal growths in his brain and spinal cord.
There have been reports in rodents of the development of tumors following the injection of pluripotential embryonic stem cells into recipient animals, although the risk of such tumors can be reduced if the cells are differentiated before being injected. However, this report is the first documented example of such a complication in a human following neural fetal stem cell therapy.
The spinal cord growth was surgically removed and this was shown to resemble a glioneuronal tumor – a type of benign neural tumor. The authors describe the process by which they analyzed the tumor and documented that it could not have arisen from the patient's own tissues. For example, the tumor contained both XX (female) and XY (male) cells and had two normal copies of the ATM gene (the gene causing Ataxia Telangiectasia, which was mutated in the patient).
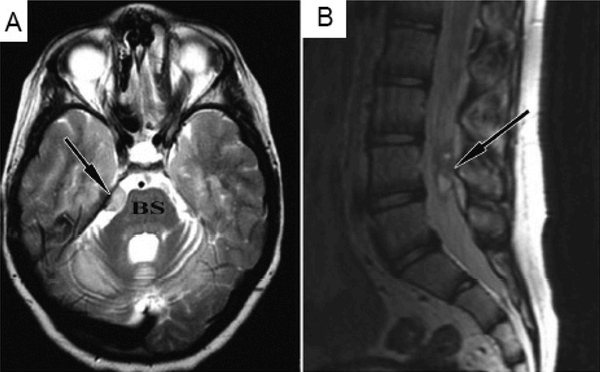
(A) Brain MRI (T2) demonstrating a lesion (arrow) based on the tentorium, next to the brain stem (BS). (B) Spinal-lumbar MRI (T2) showing intradural lesion (arrow), at the level of the L4 vertebra. From: Donor-Derived Brain Tumor Following Neural Stem Cell Transplantation in an Ataxia Telangiectasia Patient Amariglio N, Hirshberg A, Scheithauer BW, Cohen Y, Loewenthal R, et al. PLoS Medicine Vol. 6, No. 2, e29 doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000029
The authors discuss the extremely rare nature of this side effect and speculate that the patient's underlying condition may itself have allowed the tumor to become established, since individuals with Ataxia Telangiectasia often have an impaired immune system.
Although this report indicates the need for caution in stem cell therapy, the authors conclude that their findings "do not imply that the research in stem cell therapeutics should be abandoned. They do, however, suggest that extensive research into the biology of stem cells and in-depth preclinical studies, especially of safety, should be pursued in order to maximize the potential benefits of regenerative medicine while minimizing the risks."
Citation: Amariglio N, Hirshberg A, Scheithauer BW, Cohen Y, Loewenthal R, et al. (2009) Donor-derived brain tumor following neural stem cell transplantation in an ataxia telangiectasia patient. PLoS Med 6(2): e1000029. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000029