There is bad news for those planning to go to Mars in the near future: a study in mice has suggested that radiation in space could cause cognitive decline in astronauts. However, we know from past research that mental, social and physical exercise can boost cognitive functions. With planned Mars missions moving ever closer, it might be be worth exploring activity as a way to counter radiation damage.
There are many hurdles to overcome to get to Mars. The obvious one, of course, is the amount of time it takes – about eight months. But for those brave enough to attempt such a journey, this may…
Neuroscience

There is discussion of a U.S. manned mission to Mars but if recent history is any indication, the next president will undo the space program of the current one, just as the current one undid the manned space program of the last.
It may be for the best, at least as far astronaut safety is concerned. The destructive particles in galactic cosmic ray exposure can forever impair cognition, according to an oncology paper in Science Advances.
Researchers have found that exposure to highly energetic charged particles - much like those found in the cosmic rays that bombard astronauts during…
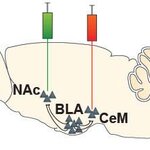
Neuroscientists have discovered brain circuitry for encoding positive and negative learned associations in mice. After finding that two circuits showed opposite activity following fear and reward learning, the researchers proved that this divergent activity causes either avoidance or reward-driven behaviors.
Prior to the new study in Nature, scientists suspected involvement of the circuits ultimately implicated, but were stumped by a seeming paradox. A crossroads of convergent circuits in an emotion hub deep in the brain, the basolateral amygdala, seem to be involved in both fear and…
Most of the time, we learn only gradually, incrementally building connections between actions or events and outcomes. But there are exceptions--every once in a while, something happens and we immediately learn to associate that stimulus with a result. For example, maybe you have had bad service at a store once and sworn that you will never shop there again.
This type of one-shot learning is more than handy when it comes to survival--think, of an animal quickly learning to avoid a type of poisonous berry. In that case, jumping to the conclusion that the fruit was to blame for a bout of illness…

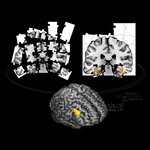
The brains of babies 'light up' like adults when exposed to the same painful stimulus, according to a small brain imaging study, and that suggests babies experience pain much like adults.
The study looked at 10 healthy infants aged between one and six days old and 10 healthy adults aged 23-36 years. Infants were recruited from the John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford and adult volunteers were Oxford University staff or students.
During the research babies, accompanied by parents and clinical staff, were placed in a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanner where they usually fell asleep. MRI scans…
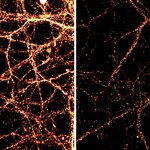
Scientists have discovered that neurons use minor "DNA surgeries" to toggle their activity levels all day, every day, and since these activity levels are important in learning, memory and brain disorders, it could shed light on a range of important questions.
"We used to think that once a cell reaches full maturation, its DNA is totally stable, including the molecular tags attached to it to control its genes and maintain the cell's identity," says Hongjun Song, Ph.D., a professor of neurology and neuroscience in the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine's Institute for Cell…

When people hear the sound of footsteps or the drilling of a woodpecker, the rhythmic structure of the sounds is striking, says Michael Wehr, a professor of psychology at the University of Oregon, and even when the temporal structure of a sound is less obvious, as with human speech, the timing still conveys a variety of important information.
Neurons in the brain use two different languages to encode information: temporal coding and rate coding.
When a sound is heard, neurons in the lower subcortical region of the brain fire in sync with the rhythmic structure of the sound, almost…

Neurons are more independent than previously believed - a finding which has implications for a range of neurological disorders and how nerve cells in the brain generate the energy needed to function.
The brain requires a tremendous amount of energy to do its job. While it only represents 2 percent of the body mass of the average adult human, the brain consumes an estimated 20 percent of body's energy supply. Unraveling precisely how the brain's cells - specifically, neurons - generate energy has significant implications for not only the understanding of basic biology, but also for…

Following a first seizure, physicians should discuss with patients whether it is appropriate to prescribe medication to reduce risk of another seizure, according to new guidelines released at the latest American Academy of Neurology meeting.
About one in 10 people worldwide - including 150,000 Americans - will experience a first seizure in their lifetime. Epilepsy is a disease characterized by one or more unprovoked seizures with a high likelihood of recurrence that are not due to another immediate triggering cause. Epilepsy affects between 2.2 and 3 million Americans, or 1 in 26 people…

Nerve cells come in very different shapes and a new paper reveals why, in insects, the cell body is usually located at the end of a separate extension.
Nerve cells follow a functional design: They receive input signals over more or less ramified cell branches (dendrites), which they forward to other nerve cells along an elongated, thin cell process (axon). The cell body contains the nucleus with genetic material and other components of the machinery that keeps the neuron alive.
Its location differs significantly between animal classes: in mammals, the cell body is usually found at a central…