New Molecules Similar To Carbohydrates Can Inhibit Enzymes In Infectious Diseases
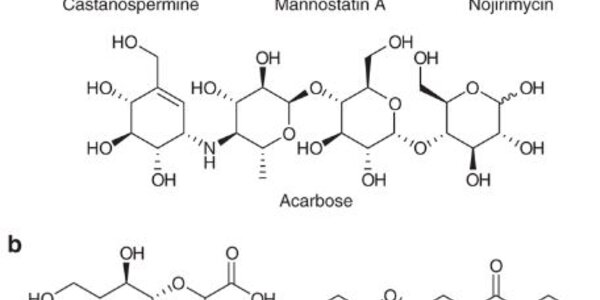
New molecules similar to carbohydrates have showed the capacity to inhibit the activity of a specific type of glycoside enzymes - and that means inhibiting infectious diseases.
Glycosides are essential enzymes to digest carbohydrates but they are also key players in infections caused by pathogens, in anti-bacterial defense and many other vital cellular processes. Because these small molecules that are able to bond with and inhibit the activity of enzymes in infectious diseases, it opens up the basis for new medicines.
“We have synthesized new molecules, taken new measurements of their…