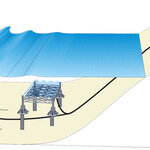
"Nobody understands the cloud," shouts a character in a recent comedy about a couple trying to remove a private video from the Internet.
In reality, the cloud is completely understandable, and it's one of few areas in climate where the emissions costs are also. And because it is quantifiable it can benefit from combinatorial optimization. the famous rucksack problem where a traveler has to try and fit everything in without leaving anything behind.
Cloud computing involves using remote servers for data storage and processing. It can provide users with more storage space and computing…