If you want to survive your hospital stay, try to avoid being admitted on the weekend.
A systematic review and meta-analysis
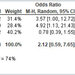
of various world regions that included 72 studies and 55,053,719 participants found that weekend admission was associated with increased morality of between 15% and 17% depending on the statistical technique used.
It must be due to higher emergency status if it is the weekend, right? Some, but the authors say the quality of care is just poorer also, which is not going to make nurses and doctors who work weekends very happy.
Subgroup analysis revealed that patients admitted during the weekend were at a higher risk of death than weekday admission in patients in almost all categories. "There are at least two potential explanations for our results. First, these differences reflect poorer quality of care in hospital at the weekend, and second, patients admitted on at weekend could be more severely ill than those admitted on at weekday. We believe that poorer care at the weekends is the much more likely explanation," write the authors.
The only exception to this trend was for the patients who underwent surgery, with the authors saying the lack of association between postoperative mortality and weekdays being potentially due to the few numbers of studies (just 4 studies) specifically examining postoperative mortality.
Furthermore, the authors say that, in some patients who underwent selected high risk procedures, these patients could received a substantial proportion of their postoperative care in critical care units that are more likely to provide the same type of service at all times during both weekdays and weekends. This would therefore dilute any effect of increased weekend mortality in these post-surgery patients.
The authors conclude: "Our systematic review shows that weekend admission is associated with higher mortality compared with weekday admission."