Imagine that you’re a young rat. You’re in the woods, doing
rat things among the dead foliage. Suddenly, off to your left, you hear a sound
that you've never heard before. It’s loud, it’s strange, and it’s… rattley.
The brain has a few jobs to do in a short amount of time.
First it has to turn the sound into a neural stimulus, digesting the sound into
its component parts—frequency, loudness, harmonics, modulations and gaps—before
it can really be comprehended. Then, the signal has to be delivered to the
areas of the brain that will help identify the sound and determine if it’s a
threat. But it’s in a rat’s best interest to react first and think later.
Little woodland creatures have no time for contemplation. So your rat brain has
two parallel auditory pathways that diverge: one goes up to the analytical centers of the cortex while the other goes directly to the emotional response
regions that modulate feelings like fear.
The place where the pathways diverge, the medial geniculate
body, or MGB, used to be thought of as a routine stop on the way up to areas
that matter more. But recent work has shown that the region is much more
complex than originally thought. In fact, it turns out that the MGBm is a fine example of the immediate frontier of basic neuroscience. The lesser-known aspects of the MGB were the
subject of a symposium at the Association for Research in Otolaryngology
meeting in Baltimore this past weekend.
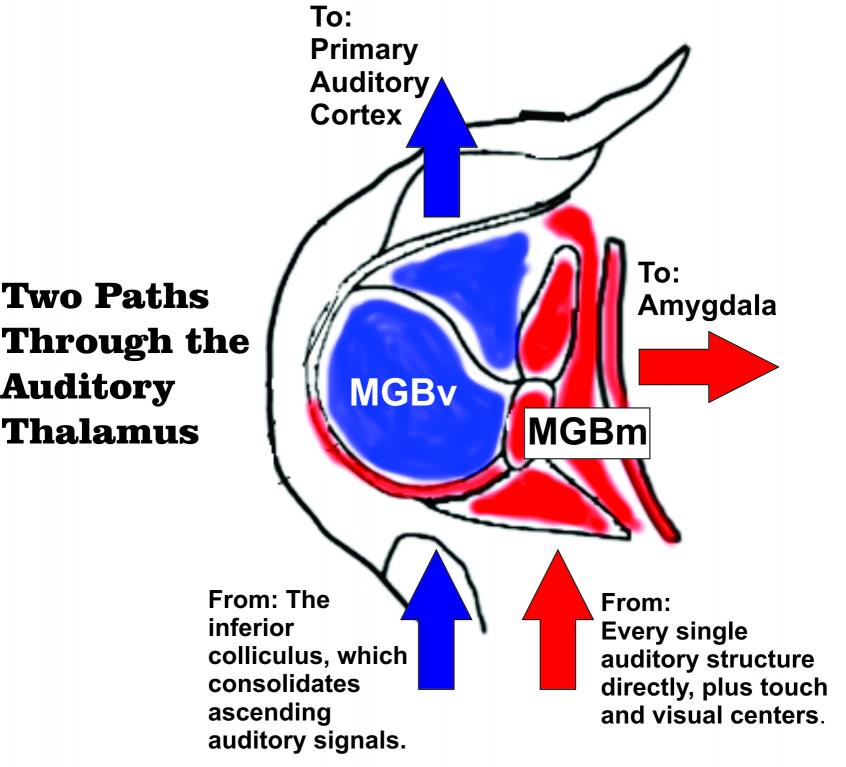
The MGB is a part of the thalamus, the central routing
station of the brain. The brain has two MGBs: a left and a right. If you cut
into the brain from ear to ear, the cross section of the MGB resembles two
round ears jutting out from the center core of the brain. The main division of
the MGB that sends up information to the primary auditory cortex is called the
ventral MGB (MGBv). The medial division (MGBm) is thinner, wrapping around the
MGBv like a shell. Its cells don’t project up to the auditory cortex. Instead,
they project to the amygdala, a region known for its involvement in emotional
processing. The MGBm is the door to the amygdala for auditory information, becoming, in a figurative sense, the "ears of our fears".
To understand how the MGBm processes signals, imagine that
you work on an assembly line. One person will make a component, the next person
will add on something, all the way down the line to you, and all the way down
to where the product is finished. The work is linear and predictable, and every
step makes some sense. Now, imagine that, instead of this stepwise procession,
every person on the assembly line take what they've been working on and dump
everything in your lap, and you are supposed to combine all of those pieces
together in a way that makes sense. And you don’t just get components from your
own assembly line.
That’s what the MGBm does. It receives direct input from
every level of the ascending auditory network, from the cochlear nucleus, where
the first digitized signals come in from the ears, to the processing centers
that individually encode the spatial and temporal features of the sound, to the
integrating centers that recombine all the digested factors of the sound for
higher-order processing, to the auditory cortex itself. All of that gets sent
directly to the MGBm directly. But that’s not all. It also gets input from the
superior colliculus, which is part of the visual system that coordinates eye
movements, and from regions of the spinal cord involved tactile senses.
It seems like the result would be a confusing, messy
conglomeration of data. And it is. Research has been lacking on MGBm neurons precisely
because their properties are frustratingly heterogenous. But the MGBm makes it
work, and scientists are getting just the first ideas about how.
Based on what we know, the consolidated MGBm signal seems to
be a kind of “significant event” detector. With its array of input, it can tell
if a sound is loud, close, and new. It can combine that information with visual
things caught by the eye, or raw input from its sense of touch, to come up with
a rough output that can tell the amygdala that something that should elicit
some kind of emotion is happening. So, the amygdala doesn’t have to wait for
the higher auditory cortex before it knows that something scary, like a
rattlesnake, is nearby—thanks to the MGBm, it can make that determination from
the raw data, and perhaps that will make the difference in saving its life.
Of course, this system is even more complex than I have
described. Not all of the regions of the MGBm overlap or connect to the same
individual neurons. And not all of the MGBm outputs go to the amygdala. The fine
details are still being worked out. In labs in Spain, Hong Kong, Britain and across the U.S., an increasing number of anatomists and physiologists are working to
find the fine details of how the MGBm works.
Why? Because it appears that the MGBm is a direct gateway
into our emotional response. So much of the way we respond to sounds around
us—a word in conversation, a bird song, a gunshot—depends on how our brains
interpret the sounds before we’re even aware that we’re hearing something. The
idea that the MGBm is the true “ear of our fears” is probably over-dramatic, but
nor is it unreasonable.
Regions like the MGBm sit on the frontier of neuroscience.
We understand things that happen in the cochlea and retina really well. We can
tap into cells in the brainstem or cortex in certain places and understand
exactly what a given neuron is encoding: a sound, a shape, a movement, a
specific memory. But in the bizarre regions just outside of these more translatable
parts of the brain, we don’t really know what the neurons are doing. We can’t
speak its language yet. By delving into the workings of the MGBm, we understand
more about the mysteries of how the brain works at higher and higher levels.
In other words, studying the MGBm may help us better
understand the mechanisms of what makes us human, even if we have to learn the
For more:
Ledoux 1998: "Organization of projections to the lateral amygdala from auditory and visual areas of the thalamus in the rat."
Weinberger 2011: "The medial geniculate, not the amygdala, as the root of auditory fear conditioning."
Bartlett 2011: "Correlation of of neural response properties with auditory thalamus subdivisions in the awake marmoset."
Anderson 2009: "Stimulus specific adaptation occurs in the auditory thalamus."
Lee 2012: "Thalamic and cortical pathways supporting auditory processing."